Observing ransomware statistics and cyber threat patterns is crucial. Research has unveiled a significant correlation between an organization’s annual revenue and its likelihood of falling victim to a ransomware attack.
Organizations with revenues ranging from $10 to $50 million experienced ransomware in cyber security attacks at a rate of 56% in the past year. This figure escalates to 72% for organizations boasting revenues of $5 billion or more.
Interestingly, the size of an organization, measured by the number of employees, does not consistently predict the likelihood of experiencing a cyber ransom attack. With the exception of the 1,001-3,000 employee segment, which saw a 73% attack rate, organizations across various sizes reported a remarkably uniform attack rate of approximately 62%.
This blog delves into the latest ransomware statistics, offering insights into these cyber threats and a guide on how to leverage data insights for preventing ransomware attacks.
Analyzing Current Ransomware Statistics
The current ransomware in the cyber security landscape reveals a shift in trends. In 2024, ransomware payments experienced a significant decline, totaling $814 million, a 35% drop from the previous year’s $1.25 billion. (Source)
This decrease is attributed to successful law enforcement actions and increased awareness among organizations. Despite this decline, the number of ransomware attacks remains high, with 5,414 published attacks on organizations worldwide, an 11% increase compared to 2023. (Source)
The industrial, consumer cyclicals, and healthcare sectors remain prime targets due to their valuable data and extensive attack surfaces. North America, Europe, and Asia are the most affected regions. The use of advanced anti-detection tools by threat actors complicates tracking and prevention, underscoring the necessity for strong cybersecurity measures.
Furthermore, attacks on major corporations, such as the Schneider Electric data breach, highlight the evolving complexity of windows ransomware. The emergence of 46 new or rebranded ransomware groups in 2024 indicates that cybercriminals are continuously refining their strategies to bypass security defenses. (Source)
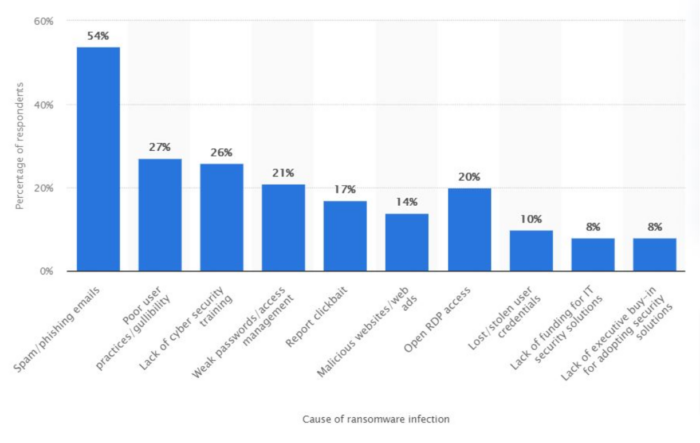
Cause of Ransomware attacks
Cost of Ransomware Attacks
The financial toll of cyber ransom attacks continues to escalate. In 2024, the average ransom demand reached $2.73 million, nearly a $1 million increase from 2023. Notably, 63% of ransom demands were for $1 million or more, with 30% exceeding $5 million. (Source)
The global average cost of a data breach has also increased, reaching $4.88 million—the highest ever recorded. Despite a slight decline in firms paying ransom (from 66% to 63%), the economic impact remains significant. (Source)
Phishing emails continue to be the predominant method of windows ransomware delivery, reported by 63% of victims. This emphasizes the critical need for robust employee training in cybersecurity practices.
However, paying ransoms remains a risky strategy. According to a survey conducted by Cyberreason in 2024, 47% of organizations that paid a ransom were able to recover their data without corruption, while 78% experienced subsequent attacks, often by the same threat actors. (Source)
This underscores the importance of preventive measures like multi-factor authentication, employee training, and comprehensive backup strategies to mitigate the financial and operational impacts of preventing ransomware attacks.
Ransomware’s Evolving Landscape
Ransomware in cyber security tactics continues to evolve as cybercriminals refine their strategies. The rise of AI-powered ransomware threats is a growing concern, enabling attackers to launch more sophisticated and elusive attacks.
However, law enforcement agencies have intensified efforts against Windows ransomware operators. In 2024, coordinated actions led to sanctions against entities supporting groups like LockBit, significantly disrupting their operations. (Source)
These efforts have contributed to a decline in overall ransom payments, demonstrating the impact of international collaboration in fighting cybercrime.
4 Effective Ways to Prevent Ransomware
Ransomware in cyber security poses a serious threat to organizations worldwide, exploiting vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access and encrypting data for ransom. Implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is crucial for preventing ransomware attacks. Here are four effective ways to fortify defenses against ransomware:
1. Implement Robust Patch Management
Regularly updating software is crucial in reducing the attack surface for ransomware. In 2024, 32% of ransomware attacks began with an unpatched vulnerability, highlighting the importance of timely updates. (Source)
2. Conduct Regular Vulnerability Scanning
Proactively identifying and remediating security weaknesses is essential. Regular scans can uncover unpatched software and vulnerabilities, enabling organizations to address them before exploitation.
3. Maintain Up-to-date Data Backup and Recovery Plans
Ensuring backups are current and stored securely off-site is a fundamental strategy for mitigating cyber ransom attacks. In case of an attack, organizations can restore affected systems promptly, reducing downtime and financial impact.
4. Employ Endpoint Protection Solutions and Cybersecurity Training
Deploying advanced security solutions and training employees to recognize phishing attempts are vital measures. Phishing emails remain a predominant windows ransomware delivery method, making ongoing employee education crucial for prevention. (Source)
By integrating these strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of ransomware in cyber security. This not only protects digital assets but also ensures operational continuity, safeguarding against unauthorized access and the devastating impact of preventing ransomware attacks.
Conclusion
The battle against ransomware in cyber security demands a data-driven approach. While law enforcement efforts have led to a decline in payments, the number of attacks remains high, demonstrating the continued threat posed by cybercriminals.
Effective patch and vulnerability management play crucial roles in mitigating windows ransomware risks. Organizations that invest in proactive cybersecurity measures such as timely patching, regular vulnerability scanning, and employee training are far better equipped to withstand cyber ransom attacks.
For personalized guidance on enhancing your cybersecurity posture, talk to our experts.