Vulnerability management in general and patch management in particular have become significant business KPIs in light of growing compliance pressures as well as the high direct and indirect costs of data breaches. Here are two cases in point (in chronological order):
- In March 2017, hackers exfiltrated hundreds of millions of customer records from the credit-reporting agency Equifax, including about 200,000 credit card numbers. The attack exploited a known Apache Struts vulnerability in a consumer-complaint web portal that should have been patched but wasn’t. Equifax has spent $1.4 billion upgrading its security, has seen its financial rating downgraded by Moody’s, and in July 2019 reached a $1.4 billion settlement with the FTC to resolve consumer claims.
- In September 2018, the Marriott Group announced that, over a four-year period, hackers had exfiltrated personal information on as many as 500 million guests, including passport and payment card numbers. The exploit had gone undetected for so long due to the poor security posture (including unpatched software) of one of Marriott’s reservation systems. In mid-2019, Marriott was fined $123 million by the UK’s GDPR office.
Despite the growing awareness of the importance of timely vulnerability remediation, many organizations are having difficulty in achieving this business-critical objective. According to the most recent ServiceNow/Ponemon survey, Costs and Consequences of Gaps in Vulnerability Response (registration required), 57% of the respondents reported that, compared to 2018, it is taking them about 20% longer in 2019 to detect and remediate a vulnerability after a patch has been released. In fact, most companies take an average of 120 days to patch vulnerabilities. And, many companies have critical vulnerabilities that go unpatched altogether. This blog post examines the key reasons why organizations are not closing vulnerability gaps quickly enough and explains how JetPatch takes vulnerability remediation to the next level.
Lack of Collaboration
According to the Ponemon survey, silo and turf issues delay patching by 12 days on average. Nine out of every 10 respondents said that they have to coordinate patching with other teams. These silo and turf issues typically arise because the security and IT teams have different mandates and different mindsets. The mandate of the security team is to maintain a high security posture, and its focus is on identifying vulnerabilities and getting them remediated as quickly as possible. The mandate of the IT team is to maintain high business continuity, and its goal is to deploy software patches in a way that will cause minimal downtime and disruption.
In addition to this inherent tension between security and IT teams, fragmented tool stacks also undermine cross-organization collaboration. Because different teams and business units use different vulnerability management tools, there is no single source of truth that can be shared across the organization. This fragmentation is particularly problematic in large organizations and even more so in organizations that have grown through mergers and acquisitions.
Lack of collaboration significantly hinders an organization’s ability to effectively remediate vulnerabilities. A prime example from the Ponemon report is that 62% of the organizations that suffered data breaches due to an unapplied patch were not aware that their organizations were vulnerable prior to the breach.
Lack of Automation
One of the key reasons for vulnerability response gaps, according to the Ponemon Report, is too much time spent navigating manual processes, especially since those manual processes take place across fragmented teams and stacks, as noted above. As shown in Figure 1, 80% of the organizations surveyed by Ponemon that have introduced automation into their vulnerability remediation processes report reduced vulnerability response times, including 56% that saw a significant reduction.
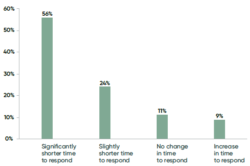
Figure 1: How automation impacted the time to respond to vulnerabilities. Source: Ponemon Report, p. 22
However, only 44% of organizations surveyed use automation in vulnerability management, with the most automated steps being prioritization and patching. Clearly there is a need for end-to-end automation solutions for vulnerability remediation that allow organizations to respond faster and smarter to vulnerabilities.
Lack of Orchestration
Unpatched vulnerabilities played a significant role in the three breach examples described in the introduction. Yet, all of these companies had vulnerability remediation and patching solutions in place. So what went wrong?
In addition to the lack of collaboration and automation, these “successful” exploits also took advantage of a lack of orchestration across the corporate vulnerability remediation ecosystem. As shown in Figure 2, for vulnerability remediation in general (and patching in particular) to be effective, it must orchestrate a plethora of related systems, from scanners and endpoint protectors to configuration managers, IT service managers, and security event managers.
Orchestration takes vulnerability response workflows to the next level of automation and collaboration. Orchestration goes beyond the automation of discrete tasks to the automation of end-to-end playbooks that take into account, for example, not just automated patch deployment, but automation tasks that should be carried out before and after patch deployment.
Another advantage of orchestration is that it aggregates vital and diverse information from many systems (threat intelligence, asset management, configuration management, and so on) to provide an enriched vulnerability response context. With orchestration, an organization no longer has to rely on a single external metric such as a CVSS score to assess a vulnerability’s criticality. By leveraging diverse external and internal data streams at scale, it is possible to pinpoint how critical a vulnerability is for that particular organization and to which IT systems.
An Intelligent, Automated Vulnerability Remediation Platform – Innovation Inside
JetPatch is an end-to-end automated patch and vulnerability remediation solution that has been designed from the ground up to address the issues that currently constrain enterprise-grade vulnerability response programs. JetPatch offers innovative, predictive technology and integrates seamlessly with all related vulnerability remediation systems in the organization’s ecosystem to provide:
- Complete visibility: Full discovery of all assets to be protected and assessment of current patching status against industry best practices and compliance requirements.
- Continuous security: Constant monitoring for new vulnerabilities and patches with alerts and automated responses.
- Innovation: Machine-learning-based Predictive Patching lets you know what the success rate of a patch cycle will be and helps you fix the issues detected (shut-down servers, credential errors, low disk space, etc.).
- Centralized governance: Consistent application of corporate patch and vulnerability remediation policies across all teams and divisions.
- End-to-end automation workflows: Recurring processes and automated rollouts that cut across silos, turfs, and fragmented tools.
- Continuous compliance: Consistent, repeatable automation workflows ensure that compliance is maintained at all times.
Summary
Vulnerability remediation must achieve the same scale and velocity as the attacks that threaten to disrupt today’s dynamic and complex IT environments. Traditional barriers to vulnerability response times–team and tool fragmentation, manual processes, and lack of ecosystem orchestration–must be torn down by end-to-end automated and orchestrated workflows that provide continuous security and continuous compliance.
Advanced technologies such as data analytics and machine learning also have important roles to play by providing context-rich criticality assessments for vulnerabilities as well as predicting vulnerability remediation outcomes.
Request a demo to see how JetPatch can accelerate your vulnerability remediation successes.