The Scope of August 2024 Patch Tuesday
The August 2024 Patch Tuesday marks a crucial update cycle, addressing 85 Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) across various Microsoft products. This month, Microsoft focused on strengthening its defenses against six critical vulnerabilities and six actively exploited zero-day vulnerabilities.
Key areas targeted by these updates include:
- Windows Operating Systems: With 43 patches applied, the Windows platform received the most attention, addressing vulnerabilities that could potentially compromise core system functions, including remote code execution and privilege escalation.
- Microsoft Office Suite: Eight patches were dedicated to Microsoft Office applications, mitigating risks particularly associated with remote code execution vulnerabilities in Excel, Outlook, and Project.
- Azure and Cloud Services: Security updates were rolled out for critical Azure services, including Azure Health Bot, highlighting the growing emphasis on cloud security within enterprise environments.
These updates also extended to Secure Boot and Windows Security, reinforcing Microsoft’s strategy to protect the integrity of its systems from the ground up. The update cycle underscores the necessity for organizations to implement these patches promptly, ensuring the security of their increasingly complex IT environments.
For more detailed guidance on the August 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, you can visit the Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) August 2024 Patch Tuesday page.
Types of Vulnerabilities Addressed
August 2024 Patch Tuesday addressed various vulnerabilities, with key focus areas being:
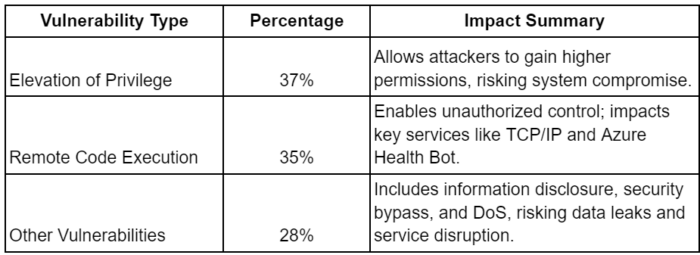
Understanding these categories helps prioritize patching efforts based on the most critical risks to your environment.
Key Vulnerabilities Addressed in August 2024
August 2024’s Patch Tuesday highlights several critical vulnerabilities that pose significant risks to both enterprise and consumer environments. Microsoft has focused on addressing six critical vulnerabilities and six actively exploited zero-day vulnerabilities, underscoring the importance of this update cycle.
Critical Vulnerabilities
- CVE-2024-38063: A remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in Windows TCP/IP, with a CVSS score of 9.8. This flaw allows an attacker to execute code remotely by sending specially crafted IPv6 packets. Microsoft recommends disabling IPv6 as a temporary mitigation.
- CVE-2024-38140: An RCE vulnerability in the Windows Reliable Multicast Transport Driver (RMCAST) with a CVSS score of 9.8. Exploitation requires a program listening on a Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) port, which may be protected by existing network controls like firewalls.
- CVE-2024-38109: An elevation of privilege vulnerability in Azure Health Bot, rated with a CVSS score of 9.1. This vulnerability could allow attackers to exploit server-side request forgery (SSRF) to gain elevated privileges within Azure’s infrastructure.
- CVE-2024-38159 and CVE-2024-38160: These RCE vulnerabilities in Windows Network Virtualization, both rated with a CVSS score of 9.1, could allow an attacker to interact with other tenants’ applications and content under certain conditions, highlighting the risks in virtualized environments.
- CVE-2023-40547: An RCE vulnerability in Secure Boot, with a CVSS score of 8.8. This vulnerability poses a risk to the integrity of the Secure Boot process, potentially allowing unauthorized code to run during system startup.
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
- CVE-2024-38189: A remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Project with a CVSS score of 8.8. Exploitation requires user interaction, such as opening a malicious file, and the vulnerability has been actively exploited in the wild.
- CVE-2024-38193: An elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock, rated with a CVSS score of 7.8. This zero-day vulnerability allows attackers to gain SYSTEM-level privileges and has been actively exploited.
- CVE-2024-38107: An elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Power Dependency Coordinator, with a CVSS score of 7.8. This vulnerability has also been exploited in the wild, allowing attackers to elevate privileges in affected systems.
- CVE-2024-38178: A scripting engine memory corruption vulnerability, rated with a CVSS score of 7.5, affecting users operating in Edge’s Internet Explorer mode. This zero-day vulnerability can be triggered by visiting a compromised URL, leading to remote code execution.
- CVE-2024-38106: A complex elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Kernel, with a CVSS score of 7.0. Despite the complexity, it has been exploited in the wild, enabling attackers to escalate privileges to SYSTEM level.
- CVE-2024-38213: A security feature bypass vulnerability in Windows Mark of the Web, with a CVSS score of 6.5. This vulnerability allows attackers to bypass Windows SmartScreen, enabling the execution of malicious files without user warnings.
Each of these vulnerabilities represents a significant risk, especially those actively exploited in the wild.
Impact on Microsoft IoT and Enterprise Security
August 2024 Patch Tuesday highlights the critical need to secure IoT and enterprise environments. Vulnerabilities in Azure IoT, Health Bot, and Windows Network Virtualization pose significant risks. Timely patching and a comprehensive security strategy are crucial to protecting these integrated technologies.
Microsoft IoT Vulnerabilities
One of the critical focuses in this patch cycle is on the vulnerabilities affecting Microsoft’s IoT infrastructure. These vulnerabilities, if exploited, could potentially allow attackers to gain control over connected devices, disrupt operations, or steal sensitive data.
- Azure IoT and Azure Health Bot Vulnerabilities:
The elevation of privilege vulnerability in Azure Health Bot (CVE-2024-38109) is particularly concerning for organizations that rely on cloud-based IoT services.
This vulnerability could allow attackers to gain elevated privileges within Azure, potentially leading to unauthorized access to IoT devices and the data they handle. With a CVSS score of 9.1, it is imperative for organizations using Azure IoT services to apply this patch immediately.
Enterprise Security Implications
The vulnerabilities addressed in August 2024 also have broad implications for enterprise security, particularly in environments that rely heavily on Windows-based systems and cloud services.
- Windows Network Virtualization:
The critical vulnerabilities in Windows Network Virtualization (CVE-2024-38159 and CVE-2024-38160) highlight the risks associated with virtualized environments.
These vulnerabilities, each with a CVSS score of 9.1, could allow an attacker to interact with other tenants’ applications and data within a shared virtualized infrastructure. For enterprises leveraging virtualization technologies, these vulnerabilities pose a severe risk, making immediate patching crucial.
- Secure Boot Integrity:
The Secure Boot vulnerability (CVE-2023-40547) addressed this month has significant implications for the integrity of enterprise systems. Secure Boot is designed to prevent unauthorized code from executing during the boot process, a critical security measure in enterprise environments where system integrity is paramount.
The identified vulnerability could allow attackers to bypass these protections, potentially leading to system compromise at the most fundamental level.
Key Enhancements to Secure Boot and Windows Security
The August 2024 Patch Tuesday also introduced several critical updates aimed at enhancing the security of Windows systems, particularly through improvements to Secure Boot and Windows Security features. These updates are vital for maintaining the integrity of systems and ensuring robust defense mechanisms against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Secure Boot Enhancements
This month, Microsoft addressed a significant vulnerability (CVE-2023-40547) in the Secure Boot process, which had a CVSS score of 8.8. This vulnerability could potentially allow unauthorized code to run during the boot process, bypassing the protections that Secure Boot is meant to provide.
- CVE-2023-40547:
The Secure Boot vulnerability identified this month poses a risk to the fundamental security of the system. Exploitation of this flaw could allow attackers to load malicious code at the earliest stages of the boot process, compromising the system before it even fully loads.
Microsoft’s patch includes updates to the Secure Boot mechanism to block this vulnerability, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a secure boot process to protect against rootkits and other types of persistent malware.
- SBAT Update:
Alongside the patch, Microsoft has implemented a Secure Boot Advanced Targeting (SBAT) update, which specifically targets vulnerable Linux boot loaders that could be exploited to bypass Secure Boot protections. This enhancement is particularly crucial for environments running dual-boot configurations or using Linux-based systems alongside Windows.
Windows Security Enhancements
Beyond Secure Boot, the August 2024 updates also brought significant improvements to Windows Defender and other core security features, strengthening the overall security posture of Windows systems.
- Windows Defender Updates:
Microsoft has enhanced Windows Defender’s capabilities by updating its threat detection algorithms and expanding its signature database.
These updates improve the system’s ability to detect and neutralize new and evolving threats more effectively. The integration with cloud-based analytics has also been strengthened, providing real-time threat intelligence that helps to preemptively block emerging threats.
- Kernel-Level Security:
The patch also included updates to kernel-mode drivers, addressing several vulnerabilities that could be exploited to gain unauthorized access to system resources. These updates are critical in preventing privilege escalation attacks that target the core of the operating system.
As attackers continue to develop more advanced techniques, the ability to prevent unauthorized code execution from the very start of the boot process and to detect sophisticated threats through improved security tools is essential.
For enterprises, these updates highlight the importance of staying current with security patches and leveraging advanced security features like Secure Boot and Windows Defender. These enhancements not only protect individual systems but also contribute to the overall security of the enterprise environment by reducing the potential attack surface.
How to implement August 2024 Security Updates
- Focus on critical and zero-day vulnerabilities, assessing their impact on your specific environment.
- Backup systems and test patches in a sandbox environment before deploying them. Use automated tools like JetPatch for consistent, efficient deployment.
- Continuously monitor systems post-deployment using tools like Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager to ensure successful updates.
- Adjust protocols and train staff to align with the latest security measures.
The Solution
Managing the complex array of patches in the August 2024 update can be challenging, particularly when balancing the need for immediate action with the operational demands of your organization. Automated patch management solutions can simplify this process by ensuring that updates are applied quickly and consistently across all systems.
Key Advantages:
- Automation: Reduce the manual workload on IT teams, ensuring that critical updates are not delayed due to human error or resource constraints.
- Visibility and Control: Real-time insights into patch compliance across your organization, allowing you to monitor the status of each update and quickly address any gaps in your security posture.
- Risk Mitigation: With features like phased rollouts and automated backup integration, minimize the risk of disruption during patch deployment, ensuring that your systems remain secure without compromising operational continuity.
Incorporating JetPatch’s patch management solution can enhance your ability to respond to vulnerabilities effectively. Know how.


