Microsoft’s December 2024 Patch Tuesday highlighted 74 CVEs, addressing a wide spectrum of vulnerabilities, with 16 rated as critical and including one zero-day vulnerability that was actively exploited.
The Scope of December 2024 Patch Tuesday
This rollout addressed 74 vulnerabilities, including 2 critical flaws identified as “Exploitation More Likely.” These vulnerabilities highlight Microsoft’s continued effort to bolster system security and mitigate cyber risks.
Here’s a breakdown of key critical vulnerabilities addressed this month:
- Windows Common Log File System Driver (CVE-2024-49088): Rated 7.8, this vulnerability is classified as “Exploitation More Likely.” It posed risks of elevation of privilege and was addressed to ensure safer system logging mechanisms.
- Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver (CVE-2024-49114): Also rated 7.8, this critical flaw was resolved to prevent potential system exploitation related to cloud file management.
Additional Notable Categories
While not all vulnerabilities were critical, the remaining issues spanned the following key areas:
- Elevation of Privilege (EoP): Multiple vulnerabilities resolved to enhance user and system security.
- Remote Code Execution (RCE): Addressed across several Microsoft services, reinforcing protection against unauthorized access.
- Denial of Service (DoS): Mitigated vulnerabilities to maintain system reliability and availability.
Key Vulnerabilities Addressed in December 2024
This section provides an overview of the vulnerabilities patched in the December 2024 security updates, categorized by their nature and potential impact:
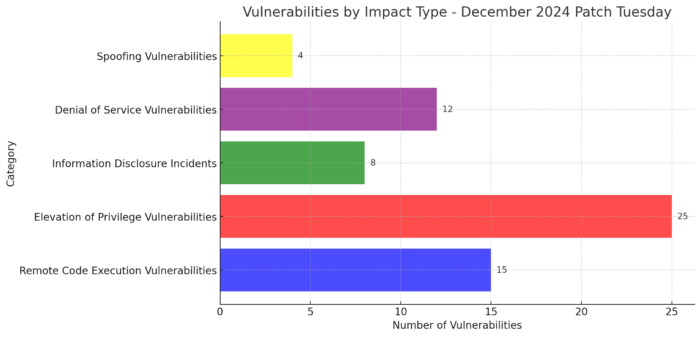
- Remote Code Execution (RCE): 15 vulnerabilities were addressed, including critical issues in Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (e.g., CVE-2024-49104, CVSS 8.8). These vulnerabilities posed significant risks, enabling attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely. Prioritizing patching systems with external-facing applications is recommended.
- Elevation of Privilege (EoP): 25 vulnerabilities were mitigated, such as those affecting the Windows Common Log File System Driver (e.g., CVE-2024-49088, CVSS 7.8, “Exploitation More Likely”). These could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to higher-privilege accounts, emphasizing the need for thorough patch application in environments with shared resources.
- Denial of Service (DoS): 12 vulnerabilities were resolved that could lead to system crashes or service interruptions, including those impacting Windows Message Queuing (e.g., CVE-2024-49122, CVSS 8.1). Maintaining high system uptime and availability depends on applying these updates promptly.
- Information Disclosure: 8 vulnerabilities were patched, such as in Windows Wireless Wide Area Network Service (e.g., CVE-2024-49081, CVSS 6.6). These issues risk exposing sensitive data to unauthorized actors, which is critical in compliance-heavy industries.
- Security Feature Bypass (SFB): 4 vulnerabilities affecting systems like Windows Virtualization-Based Security (e.g., CVE-2024-49076, CVSS 7.8) were mitigated to ensure integrity in secure environments relying on hardware-backed isolation.
Recommended Actions:
- Prioritize addressing “Exploitation More Likely” vulnerabilities (e.g., CVE-2024-49088, CVE-2024-49093) to minimize exploitation risks.
- Use automated patch management solutions to streamline the application of updates across all systems, particularly in large-scale environments.
In-Depth Analysis of Critical Vulnerabilities
December 2024 Patch Tuesday provided detailed insights on significant vulnerabilities, notably CVE-2024-49090 and CVE-2024-49114, both of which were noted as “More Likely” to be exploited, reflecting their critical impact on system security.
These vulnerabilities are pivotal due to their potential effects on the integrity and confidentiality of the systems:
- CVE-2024-49090 (Windows Common Log File System Driver): A high-severity issue with a CVSS score of 7.8. It could allow attackers to gain elevated privileges, significantly compromising system security and data integrity.
- CVE-2024-49114 (Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver): Also with a CVSS score of 7.8, this vulnerability could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the local system, posing a severe threat to system operations.
| CVE ID | Impact | Severity Score | Previously Exploited? |
| CVE-2024-49090 | Elevation of Privilege | 7.8 | Yes |
| CVE-2024-49114 | Arbitrary Code Execution | 7.8 | Yes |
Secure Boot and Windows Security Enhancements
- Windows Defender for Endpoint Improvements
This update addresses vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-49057 (CVSS 8.1), which enhance Windows Defender’s threat detection algorithms. These updates utilize the latest threat intelligence databases, bolstering defenses against advanced malware and ransomware attacks. - Enhanced Real-Time Monitoring
Vulnerabilities such as CVE-2024-49122 and CVE-2024-49093 address performance and stability within Windows components, optimizing real-time threat detection and mitigation mechanisms. - System Compatibility and Stability Enhancements
Critical vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-49072 (Windows Task Scheduler) and CVE-2024-49119 (Windows Remote Desktop Services) ensure compatibility with modern systems and reduce risks from outdated configurations. These updates improve system stability and operational efficiency.
Practical Guide: Implementing December 2024 Security Updates
This month’s updates address 74 vulnerabilities, including high-priority issues such as CVE-2024-49112 (Windows LDAP – CVSS 9.8) and CVE-2024-49093 (Resilient File System – CVSS 8.8). Here’s a tailored guide to effectively implement these updates:
1. Pre-Deployment Testing
- Test updates like CVE-2024-49093 in isolated environments. Systems utilizing the Windows Resilient File System may face unique dependencies. Controlled testing can preempt compatibility issues, especially in legacy setups.
2. Prioritization of Critical Vulnerabilities
- Deploy patches for CVE-2024-49122 (Windows Message Queuing) immediately due to its potential exploitation history.
- Prioritize updates to CVE-2024-49119 (Remote Desktop Services), which could impact critical remote operations infrastructure.
- Use the CVSS scores and exploitability indices in the release notes to guide decisions on patching order.
3. Streamlined Deployment
- Leverage tools like WSUS, SCCM or Intune for automated patch management.
- Ensure phased deployments for complex infrastructures, starting with non-critical systems to validate stability.
4. Post-Update Monitoring
- For updates like CVE-2024-49057 (Microsoft Defender for Endpoint), validate deployments using system event logs to ensure no residual anomalies exist.
- Utilize advanced monitoring tools to assess update impacts on system performance, especially for sensitive configurations.
5. Secure Boot and Firmware Updates
- Organizations should synchronize firmware updates with OS patches to ensure comprehensive boot-level threat mitigation.
Conclusion
December’s Patch Tuesday addressed a total of 74 vulnerabilities, including 16 critical flaws and at least one zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2024-49112, CVSS 9.8). These updates span Microsoft services, tools, and platforms, emphasizing the critical importance of timely and strategic patch management.
For enterprises, leveraging automated patching tools ensures seamless deployment while minimizing business disruptions. To explore these updates and their implications in greater detail, here.


